

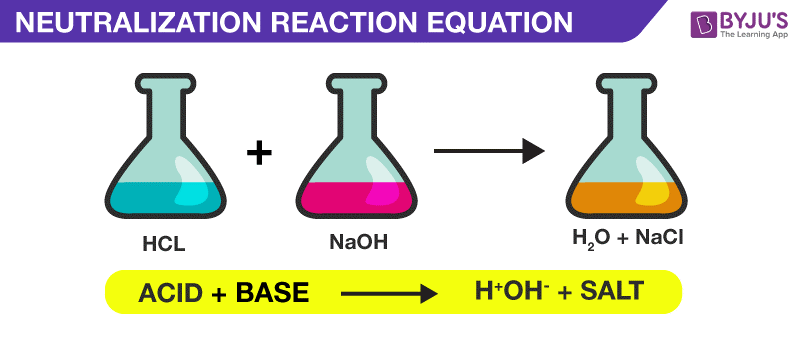
Chemical reactions are commonly written as equations:
Catalysts do not change equilibria positions. Catalysts are substances that accelerate the rate ( velocity ) of a chemical reaction without themselves being consumed or appearing as part of the reaction product. Reaction Conditions The environmental conditions, such as temperature, pressure, catalysts & solvent, under which a reaction progresses optimally.
Product(s) The final form taken by the major reactant(s) of a reaction. The portion of a reagent that ends up being incorporated in the product may range from all to very little or none. It may be organic or inorganic small or large gas, liquid or solid. Reagent: A common partner of the reactant in many chemical reactions. Most ( or all ) of the reactant molecule is normally incorporated as part of the product molecule. The reactant is often ( but not always ) the larger and more complex molecule in the reacting system. Other compounds may also be involved, and common reactive partners ( reagents ) may be identified. Reactant or Substrate: The organic compound undergoing change in a chemical reaction. We begin by defining some basic terms that will be used frequently as this subject is elaborated.Ĭhemical Reaction: A transformation resulting in a change of composition, constitution and/or configuration of a compound ( referred to as the reactant or substrate ). Now that we can recognize these actors ( compounds ), we turn to the roles they are inclined to play in the scientific drama staged by the multitude of chemical reactions that define organic chemistry. Organic chemistry encompasses a very large number of compounds ( many millions ), and our previous discussion and illustrations have focused on their structural characteristics.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
